In recent years, both the Paleo and plant-based diets have surged in popularity, each promising unique health benefits and a pathway to improved well-being. While both have garnered significant attention, they differ greatly in their core principles, food choices, and long-term sustainability. This article aims to provide a balanced perspective on both diets, exploring their foundations, benefits, criticisms, and potential for combination, to help readers make informed decisions aligned with their personal needs and goals.
Are you curious about the best diet for your health and the planet? You’ve come to the right place! There are several options that can be confusing. The NiMe diet is a plant-based diet that focuses on improving your gut health, while the Paleo diet tries to emulate how our ancestors ate and is often high in meat. There are also vegan diets that exclude all animal products, and vegetarian diets that exclude meat.
But, which is right for you? It’s not always a clear answer. To really understand the differences, potential benefits and drawbacks, and how these diets could work for you, please keep reading. I’ve got lots of details about the NiMe, Paleo, vegan, and even “Pegan” diets to help you make the best choice. You’ll learn about the science behind them, what foods to include and exclude, and more!
Defining the Paleo Diet
The Paleo diet, often referred to as the “caveman diet,” is rooted in the concept of eating as our Paleolithic ancestors did. This means focusing on whole, unprocessed foods that were available before the advent of agriculture. The diet emphasizes natural, fresh foods including:
- Meats, preferably wild-caught
- Seafood
- Eggs
- Vegetables
- Fruits
- Nuts
- Seeds
- Healthy fats
Conversely, the Paleo diet excludes:
- Grains (both refined and whole)
- Legumes
- Packaged snacks
- Dairy
- Sugar
- Processed foods
It is seen not just as a diet, but a lifestyle that stresses high food quality and sustainability.
Defining Plant-Based Diets
Plant-based diets focus on foods primarily derived from plants. It is important to note that “plant-based” is not always synonymous with veganism or vegetarianism. The term “plant-based” has become a “rallying cry” and may not always represent a reasonable nutritional philosophy. There are various types of plant-based diets, each with different levels of restrictions:
- Vegan: Excludes all animal products, including meat, eggs, and dairy.
- Vegetarian: Excludes meat, fish, and poultry .
- Lacto-ovo-vegetarian: Allows eggs and dairy
- Lacto-vegetarian: Allows dairy but excludes eggs
- Ovo-vegetarian: Allows eggs but excludes dairy
- Pescatarian: Allows fish, with limited eggs and dairy
- Flexitarian: Primarily vegetarian but occasionally includes meat, fish, or poultry
A key point is that the term “plant-based” doesn’t automatically mean “healthy,” and many processed junk foods can be plant-based.
The Paleo Diet’s Focus
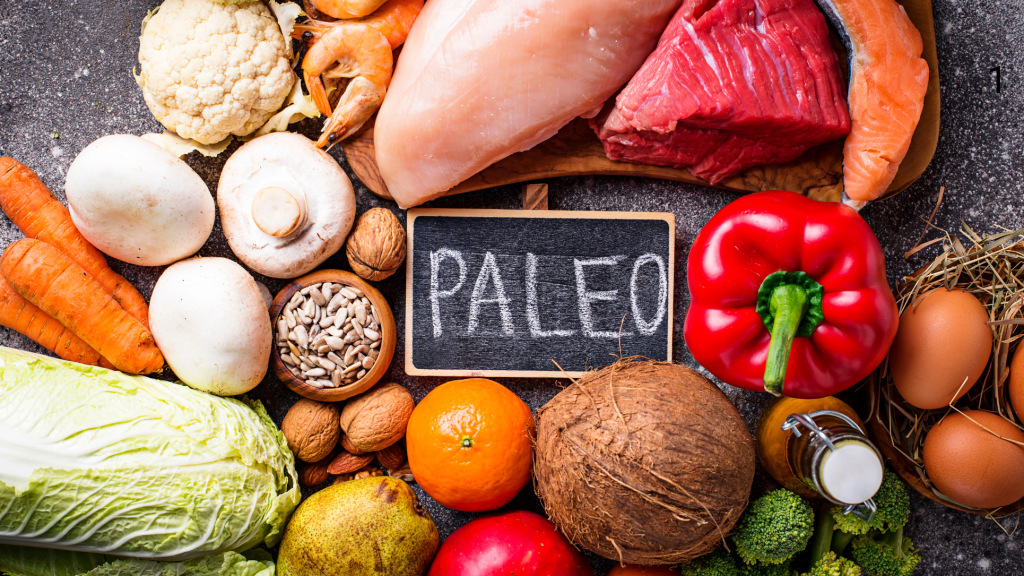

The Paleo diet is designed to mimic the eating habits of our Paleolithic ancestors by emphasizing consumption of unprocessed whole foods including wild-caught meats that are high in omega-3 fats.
Special: Create Your Own Paleo Diet…More HERE
The Plant-Based Focus
Plant-based diets emphasize foods primarily from plants, such as fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, oils, whole grains, legumes, and beans.
Criticisms of the Paleo Diet
Despite its popularity, the Paleo diet faces criticism for several reasons:
- It excludes entire food groups such as grains and legumes.
- Its restrictive nature can lead to potential nutrient deficiencies.
- It can cause digestive issues like constipation or diarrhea.
- The high reliance on animal protein raises concerns about sustainability and long-term health impacts.
- Many people following a Paleo diet consume too much meat, toxic animal substances and do not prioritize organic options.
Criticisms of Plant-Based Diets
Plant-based diets also come with their own set of criticisms:
- Sustaining a strict plant-based diet long-term can be challenging.
- There’s a potential for deficiencies in essential nutrients like vitamin B12, certain amino acids, zinc, and vitamin D.
- These deficiencies must be addressed with supplementation, fortified foods or protein powders.
Health Benefits of the Paleo Diet
The Paleo diet has shown potential benefits in the short term:
- Improved body weight, satiety, lipid profiles, blood glucose, insulin sensitivity, inflammation, and blood pressure.
- Lower total cholesterol levels.
- Reduced inflammation.
- Weight loss.
- Increased energy levels.
It’s important to note that clinical trial Paleo diets are carefully designed and different from popular Paleo diets. Clinical diets eliminate processed foods, refined sugars and fats, and focus on vegetables, fruits, nuts, and seeds with lower fat and saturated fat content. However, long-term effects of the Paleo diet still remain a concern.
Health Benefits of Plant-Based Diets
Plant-based diets offer many potential health benefits:
- Improved energy levels.
- Alkalization of the body.
- Potential for reversing certain diseases and types of cancer.
- Positive impact on gut microbiome diversity which influences digestion, immunity and metabolism.
Special: Cook Ridiculously Tasty Vegan Recipes…More HERE
The NiMe Diet: An Alternative Approach
The NiMe (Non-Industrialized Microbiome Restore) Diet is a newer approach focused on gut health and microbiome restoration. This diet aims to mimic the traditional, non-industrialized dietary habits while incorporating modern understanding of diet-microbiome interactions. The NiMe diet includes Lactobacillus reuteri and emphasizes fiber-rich plant-based foods while excluding dairy, beef, and wheat. Measurable health improvements have been observed with the NiMe diet:
- Reduction in LDL cholesterol, blood sugar levels, and inflammation markers.
- Weight loss achieved by supporting gut health without calorie restriction.
- Improved microbiome diversity and reduced pro-inflammatory bacteria.
The Pegan Diet: A Hybrid Approach
The “pegan” diet combines principles from both Paleo and vegan eating plans. This approach prioritizes vegetables and fruits, while also including moderate amounts of meat, fish, nuts, seeds, and some legumes. The pegan diet is less restrictive than either Paleo or vegan.
Is a Vegan Paleo Diet Possible?

Combining vegan and Paleo diets is possible with a flexible mindset. A strict vegan Paleo diet is not 100% Paleo, and requires flexibility and a willingness to modify traditional restrictions. The main challenge involves excluding both animal products and traditional paleo foods like grains and legumes, creating a potential for nutritional deficiencies. A modified vegan Paleo diet may include certain low-carb, high-protein grains like quinoa, amaranth, and buckwheat.
Here’s a list of foods typically included in a vegan Paleo diet:
- Leafy greens and non-starchy vegetables: broccoli, kale, peppers, onions, carrots, tomatoes
- Starchy vegetables and fruits: potatoes, sweet potatoes, yams, turnips, apples, bananas, oranges, pears, avocados, strawberries, blueberries
- Protein sources (nuts and seeds): almonds, macadamia nuts, walnuts, hazelnuts, sunflower seeds, pumpkin seeds
- Healthy fats: olive oil, coconut oil, avocado oil, almond oil
Concerns about Meat Consumption
The consumption of meat, a cornerstone of the Paleo diet, raises several health concerns:
- Meat can contain agrochemicals, endotoxins, environmental contaminants, heme iron, hormones, antibiotics, and pro-inflammatory molecules.
- High consumption of red and processed meat is associated with increased mortality and disease risk.
- Red meat and processed meats increase the risk of heart disease, cancer, and diabetes.
- The World Health Organization has classified processed meat as a Group 1 carcinogen, and red meat as a probable carcinogen.
Current recommendations advise limiting red meat and avoiding processed meat.
Nutrient Considerations
Both Paleo and plant-based diets require careful attention to nutrient intake. It is critical to obtain adequate protein, vitamins, and minerals through diet or supplementation. Vitamin B12 can be difficult to obtain on a vegan diet, and may require supplementation.
The Gut Microbiome
The gut microbiome is significantly impacted by diet, influencing digestion, immunity, and metabolism. The NiMe diet specifically targets restoring the gut microbiome by reducing pro-inflammatory bacteria and enhancing beneficial bacteria with the addition of Lactobacillus reuteri. Vegans generally have a healthier gut flora than omnivores.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of both diets is a critical consideration. It is important to know that:
- Some plant-based crops can have higher greenhouse gas emissions than animal products.
- There are concerns about GMO crops and some edible oils, such as corn, soy and canola oil.
- Some countries have adopted sustainable practices for products like palm oil, while others still damage the environment.
- Animal products can play a role in sustainable and regenerative agricultural food production.
Popular Paleo Diet Myths
Several misconceptions exist about the Paleo diet:
- The clinical trial diets are often not the same as the popular diets that many people follow.
- Popular paleo diets are less rigid and may include oils, processed meats, and salt.
- Paleo diets are often high in fat, but the original paleo diet was actually plant-based, consisting of 65% plants and 35% animal products.
- The short-term gains from a Paleo diet may come with long-term pain.
Popular Plant-Based Diet Myths
It’s also important to debunk some myths about plant-based diets:
- Not all plant-based foods are healthy.
- The term “plant-based” can sometimes be a form of “greenwashing”.
- Vegan and plant-based are not synonymous.
- A plant-based diet is not always better for the environment.
Sample Meal Plans and Recipes
Here’s a sample vegan Paleo meal plan with a few ideas to get you started:
- Breakfast: Sweet Potato Breakfast Bowl, or grain-free granola.
- Sweet Potato Breakfast Bowl: Combine cooked sweet potato with vegetable milk or water, date syrup, and cinnamon. Top with almond butter, banana, peach, and blueberries (as desired).
- Lunch: Roasted Brussels sprouts or a vegan Caesar salad.
- Roasted Brussels Sprouts with Pomegranate and Chili-Lime Sauce: Roast halved Brussels sprouts with olive oil, chili powder, salt, and pepper. Toss with lime zest, lime juice, and date syrup. Top with pomegranate seeds.
- Snack: Strawberry and Beetroot Detox Smoothie
- Strawberry and Beetroot Detox Smoothie: Blend frozen strawberries, apple juice, fresh beetroot, and frozen banana. Add optional toppings such as fresh mint, toasted coconut chips or diced apple
- Appetizer: Fresh Vegetable Salad with Oyster Mushrooms
- Fresh Vegetable Salad with Oyster Mushrooms: Sautee oyster mushrooms and season. Combine with Romaine lettuce, red cabbage, zucchini, carrots, cherry tomatoes, and avocado. Toss with a dressing made of sunflower seed butter, miso paste, oil, and warm water.
- Dinner: Sweet potato bowls or a parsnip and Brussels sprouts bake.
- Cauliflower and Sweet Potato Curry: Sautee diced sweet potatoes and cauliflower. Separately, sautee ginger, onion, and garlic with spices, then add tomatoes and tomato paste. Combine the vegetables and simmer with water.
- Dessert: Pegan Chocolate
- Pegan Chocolate: Combine coconut oil, date syrup, coconut chips, sunflower or pumpkin seeds, cocoa powder, and sea salt in a food processor. Form bars and freeze until firm.
Conclusion
Both the Paleo and plant-based diets offer unique approaches to eating, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. The Paleo diet emphasizes whole, unprocessed foods while excluding grains and legumes. Plant-based diets focus on foods primarily from plants with different levels of restrictions. The NiMe diet offers an alternative approach that targets the gut microbiome. The pegan diet can be a useful hybrid. It’s essential to consider individual nutritional needs, health goals, ethical concerns, and lifestyle preferences when choosing the right diet. Combining both diets can be done successfully with proper planning and discipline. Ultimately, the best diet is one that is sustainable, balanced, and supports overall well-being.
FAQ
General Dietary Approaches
- What is the NiMe Diet?
The NiMe (Non-Industrialized Microbiome Restore) Diet is a plant-based dietary approach that emphasizes the eating habits of non-industrialized societies, with a particular focus on improving gut health. It is rooted in scientific research and incorporates Lactobacillus reuteri ( L. reuteri), a beneficial bacterium. - How does the NiMe Diet differ from the Paleo diet?
While both diets focus on whole, unprocessed foods, the NiMe Diet is plant-based, excluding dairy, beef, and wheat. The Paleo diet often includes significant amounts of animal protein and excludes grains and legumes. The NiMe Diet is also specifically designed to improve gut health, whereas the Paleo diet is based on the presumed eating habits of Paleolithic ancestors. - What is the Paleo diet?
The Paleo diet is based on the eating habits of Paleolithic ancestors, which includes meat, seafood, eggs, fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, and healthy fats and oils while excluding grains, legumes, dairy, and processed foods. - What is a plant-based diet?
A plant-based diet focuses on foods primarily from plants, including fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, oils, whole grains, and legumes. It may or may not include animal products. - What is a vegan diet?
A vegan diet excludes all animal products, including meat, dairy, eggs, and honey. - What is a vegetarian diet?
A vegetarian diet excludes meat, fish, and poultry, but may include eggs and/or dairy. There are many different kinds of vegetarian diets, some that include eggs or dairy. - What is the Pegan diet?
The Pegan diet combines elements of both Paleo and vegan diets, emphasizing plant-based foods while including moderate amounts of nuts, seeds, some legumes, and potentially some fish or animal products.
Health Benefits and Outcomes
- What are the main health benefits of the NiMe Diet?
The NiMe Diet has been shown to reduce LDL cholesterol by 17%, decrease blood sugar levels by 6%, and lower C-reactive protein (an inflammation marker) by 14%. It also promotes weight loss by improving gut health rather than restricting calories. - How does the NiMe Diet impact the gut microbiome?
The NiMe Diet enhances gut microbiome diversity, reduces pro-inflammatory bacteria and harmful bacterial genes, and promotes the presence of beneficial bacteria such as L. reuteri. - What are the health benefits of a Paleo diet?
A Paleo diet can improve total cholesterol, reduce inflammation, aid in weight loss, and increase energy levels by focusing on whole foods and limiting processed foods. - What are the health benefits of a plant-based diet?
Plant-based diets can provide more enzymes, vitamins, and minerals, and can improve energy levels, alkalize the body, and reverse certain diseases. - Is a vegan diet healthy?
A vegan diet can be healthy but may lack certain nutrients like vitamin B12, amino acids, and zinc. These deficiencies can be addressed with supplements and a well-planned diet. - Does a vegan diet improve gut health?
Yes, a vegan diet can improve gut health and gut flora. - What are the short-term benefits of the Paleo diet?
Short-term benefits of a Paleo diet include weight loss and improved lab results. - What are the potential long-term risks of the Paleo diet?
Long-term adherence to a diet high in animal protein is associated with increased mortality and cardiovascular disease risk.
Dietary Components and Concerns
- What foods are excluded from the NiMe Diet?
The NiMe Diet excludes dairy, beef, wheat, and highly processed foods laden with sugar and saturated fats. - What foods are excluded from the Paleo Diet?
The Paleo diet excludes grains, legumes, dairy, processed sugar, and processed foods. - What foods are emphasized in the NiMe diet?
The NiMe diet emphasizes diverse, fiber-rich foods, with a focus on plant-based options, particularly vegetables, legumes, and other whole plant ingredients. - What are the main food groups in a vegan diet?
A vegan diet consists of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts and seeds. - What foods are typically included in a Pegan Diet?
The Pegan diet includes abundant leafy greens, non-starchy vegetables, starchy vegetables and fruits, nuts, seeds, healthy fats and some legumes, and sometimes fish or animal products. - What are the concerns about meat consumption?
Meat consumption is associated with various health concerns, including increased risk of cancer, cardiovascular disease, and diabetes. Meat also contains toxins, environmental contaminants, and pro-inflammatory molecules. - Does meat provide essential nutrients?
While meat contains nutrients like vitamin B12 and K2, these can also be obtained from other sources, such as fortified foods, supplements, and plant-based conversion of K1 to K2. - What are the concerns about a long term vegan diet?
Long term vegan diets can lead to deficiencies in vitamin B12, certain amino acids, zinc and vitamin D. - Can a vegan diet lead to B12 deficiency?
Yes, a vegan diet may lead to B12 deficiency because B12 is primarily found in animal products. Vegans can obtain B12 from fortified foods or supplements. - Can you get enough protein on a plant-based diet?
Yes, adequate protein can be obtained through a well-planned, diverse plant-based diet.
“Plant-Based” Misconceptions
- Is “plant-based” always healthy?
No, the term “plant-based” can be misleading. It doesn’t automatically mean “healthy” because many processed junk foods are plant-based. The term is also used interchangeably with “vegan”, which may not always be healthy. - Is the Paleo diet plant-based?
The original Paleo diet was primarily plant-based, consisting of approximately 65% plants and 35% animal foods. - Are all “plant-based” crops environmentally sustainable?
No, some plant-based crops, like certain cereal grains and soy, have high greenhouse gas emissions and can contribute to deforestation.
Combining Diets
- Is it possible to combine Paleo and vegan diets?
Yes, it is possible through a “Pegan” or Vegan Paleo diet, which emphasizes plant-based foods while potentially including some animal products if one is not strictly vegan. - What is a vegan paleo diet?
A vegan paleo diet combines the principles of both diets by excluding all animal products as well as grains and legumes. To be followed safely as a vegan, some grains (normally excluded on a paleo diet) are added in to ensure nutritional completeness. - Can you be a vegan and follow a Paleo diet?
Yes, with modifications, a vegan can follow a modified Paleo diet by focusing on plant-based whole foods and including certain grains for nutritional completeness, while avoiding animal products.
Practical Application
- Are there recipes available for the NiMe Diet?
Yes, recipes inspired by the NiMe Diet are available on social media platforms like Instagram and Facebook, and will be included in an upcoming online cookbook. - What are some sample Vegan Paleo meals?
Sample meals include sweet potato breakfast bowls, roasted Brussels sprouts with pomegranate, strawberry and beetroot smoothies, vegetable salad with oyster mushrooms, cauliflower and sweet potato curry, and Pegan chocolate.
Additional Points
- How do clinical trials for the Paleo diet differ from popular Paleo diets?
Clinical trials use carefully designed diets with lower fat content and higher vegetable intake compared to what most people following the Paleo diet typically eat. - What are some potential deficiencies of a vegan diet?
Some common deficiencies of a vegan diet are B vitamins and amino acids. - Do traditional diets include more than just Paleo?
Yes, a traditional diet is not just Paleo, it is broader. It includes foods like grass-fed dairy and a variety of vegetables and wild meats.
This list should provide a comprehensive overview of the key concepts and address common questions related to these different dietary approaches, according to the sources you provided. Let me know if you have any further questions.